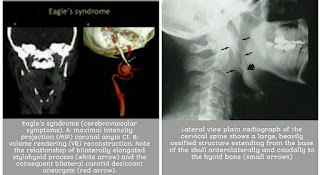
Eagle syndrome refers to symptomatic elongation of the styloid process or calcified stylohyoid ligament 1-2. It is often bilateral. In most cases, the cause is unknown; however, the condition is sometimes associated with disorders causing heterotopic calcification such as abnormal calcium/phosphorus metabolism and chronic renal failure.
Eagle syndrome (also termed stylohyoid syndrome styloid syndrome, styloid-stylohyoid syndrome, or styloid–carotid artery syndrome) is a rare condition characterized by sudden, sharp nerve-like pain in the jaw bone and joint, back of the throat, and base of the tongue, triggered by swallowing, moving the jaw, or turning .
Eagle syndrome can occur unilaterally or bilaterally and most frequently results in symptoms of dysphagia, headache, pain on rotation of the neck, pain on extension of the tongue, change in voice, and a sensation of hypersalivation We present rare and diagnostic radiographic evidence of this on both plain film radiographs and CT scans. Although well documented in otolaryngology literature and dentistry literature, this syndrome has not been reported in the radiology literature.
Credits: Vijayakumar Sadhanandham Sir















No comments:
Post a Comment
Thanks for Reading